Write Rules in Smart Forms
Write rules are continuously evaluated declarative constraints enforced during Smart Form editing.
They serve two purposes:
- Blocking validation
- Non-blocking guidance
Evaluation occurs:
- On every field change
- On every relation mutation
- On every classification change
Violation Placement Model
Field-Level Rules
Violation is rendered directly under the field that caused it.
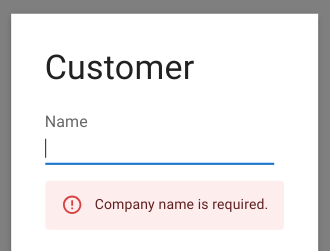
Figure: Error displayed directly under the input field for Company Name.
Relation-Level Rules
Rendered directly under the relation component.
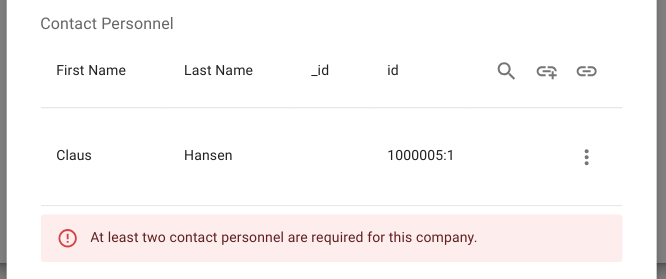
Figure: Error displayed below the relationship for Contact Personnel.
Form-Level Rules
Rendered in the form header.
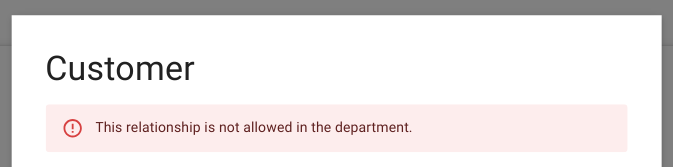
Figure: Error displayed at the top of the form for a general rule violation.
Informational (Non-Blocking) Rules
These do not prevent persistence but provide structured guidance:
- Informational messages
- Warnings
- Acknowledgements
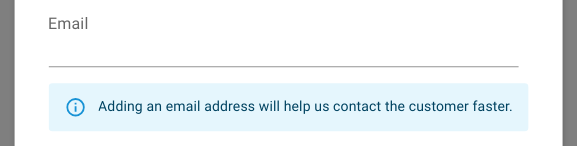
Figure: Information message about a missing email
Execution Guarantees
- Rules are evaluated before persistence
- Rules are evaluated after every mutation
- Rules always operate on the staged form state
- No database change occurs unless all blocking rules pass