The Data Navigator
Data Navigator Overview
The Data Navigator is the system’s primary interface for relation-driven traversal of the data model. It allows users to move transitively across entities by following defined relationships while maintaining full contextual traceability.
Unlike the Data Explorer, which is optimized for dataset construction and bulk analysis, the Data Navigator is optimized for record-centric navigation. It is available on both desktop and mobile, with interaction models adapted to each form factor.
The core function of the Data Navigator is to allow users to:
- Start from any record
- Traverse arbitrary relation paths
- Inspect and mutate related entities
- Maintain full navigation context at all times
Desktop Version of the Data Navigator
Navigation and Context Trail
At the top of the view, the Data Navigator displays a context trail representing the full traversal path from the initial record to the current endpoint. Each trail segment corresponds to one navigation step across a relation.
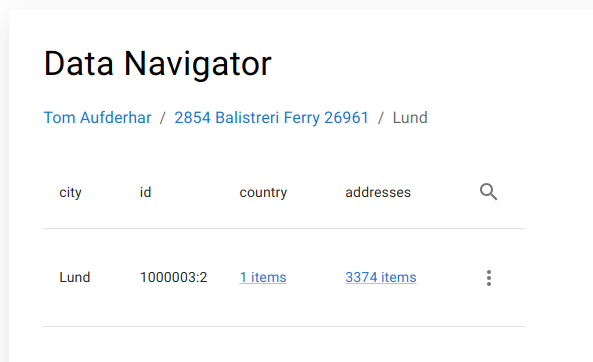
The trail is fully interactive:
- Any previous step can be revisited
- Navigation can branch from any historical node
- The last trail element always represents the currently active dataset
This provides a deterministic navigation history equivalent to a path expression evaluated step-by-step at runtime.
Filters
Below the trail, a filter selector is available. Filters are applied at the current navigation depth and restrict which rows are loaded for the active table.
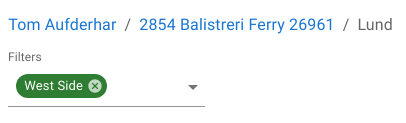
Execution characteristics:
- Each navigation step is capped at 100 rows
- Filters apply before rendering
- The cap prevents unbounded result expansion in deep traversals
Filters support both inclusive and exclusive predicates and operate on the same classification and column logic used throughout the system.
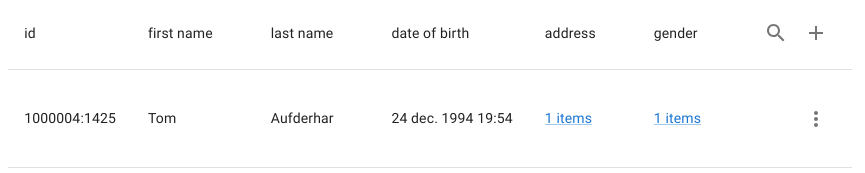
Table Display
The main view renders a relation-aware table containing:
- All configured operational columns for the active table
- The record’s unique identifier
- Outbound relation links
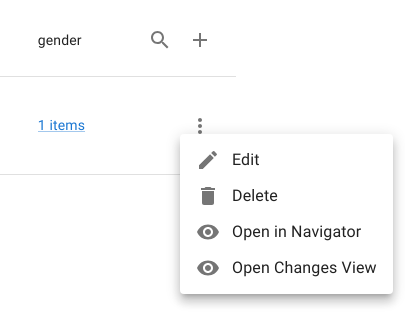
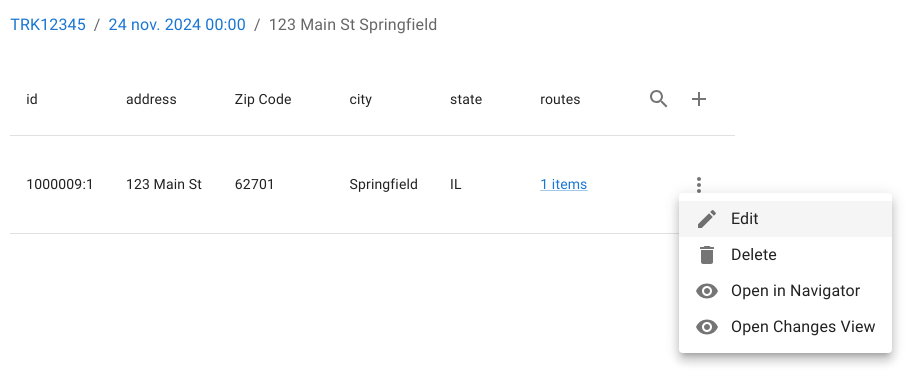
Each row exposes a row operation menu, providing record-level actions. The view also exposes:
- A create action (plus icon)
- A row filter action (magnifying glass)
Operational Example (Relation Traversal)
The Data Navigator supports full investigative workflows by chaining relations dynamically. A typical traversal pattern involves:
- Locating a root record (e.g. a package by tracking number)
- Following its route relation
- Navigating to the assigned driver
- Backtracking and traversing to the recipient
- Navigating to the associated address
- Editing the dependent entity directly
Each step is preserved in the navigation trail and can be revisited or branched without reloading the entire navigation chain.
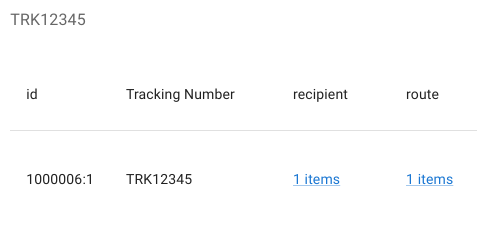
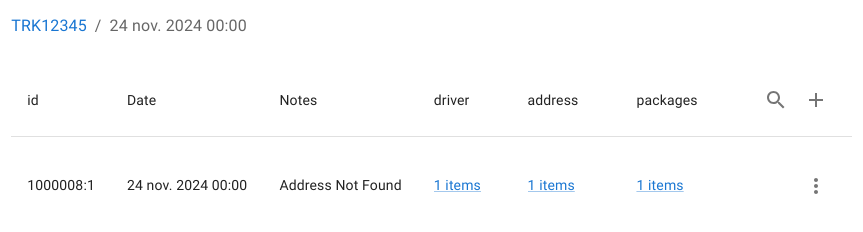
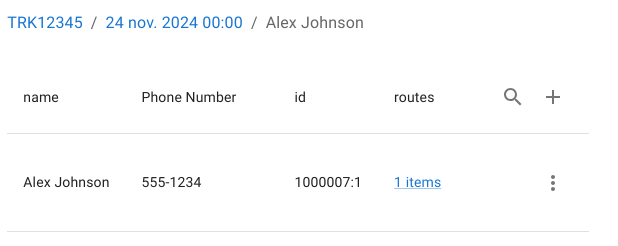
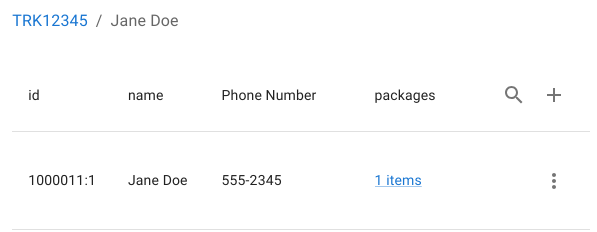
This allows full end-to-end investigation and correction across multiple dependent entities without context loss.
Mobile Version of the Data Navigator
Optimized UI for Smaller Screens
On mobile devices, the Data Navigator is rendered as a collapsed list-based interface instead of a table:
- Each row initially displays only the table’s summary columns
-
Expanding a row reveals:
-
All operational columns
- Related entities
- System columns are hidden by default

Single result view
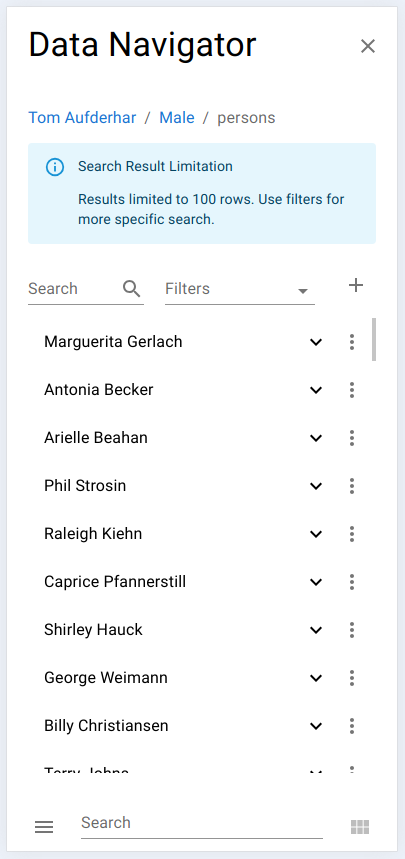
Multiple results
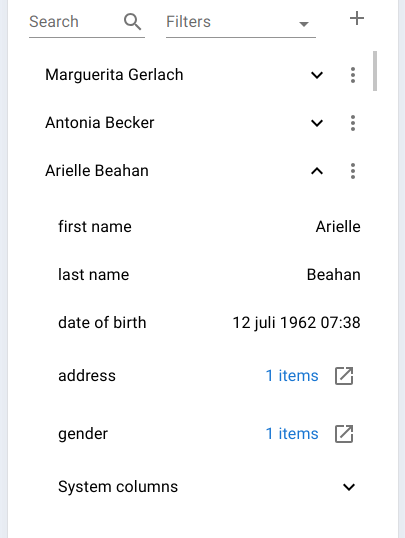
Expanded record
Navigation and Interaction
The mobile navigator preserves the same traversal semantics as the desktop version:
- All relations remain fully navigable
- Relations can optionally be opened in a new window
- Each row exposes the full record operation menu
- Record creation is supported directly from mobile
Despite the reduced screen real estate, the same underlying navigation and mutation capabilities remain available.
Summary
The Data Navigator provides a deterministic, relation-based navigation layer on top of the Minyu data model:
- On desktop, it supports multi-step investigative workflows through a table-based, trail-driven interface
- On mobile, it provides a compact, record-centric list view optimized for rapid lookup and update
Together, these two implementations expose a unified traversal engine that allows users to:
- Navigate transitive relations without query construction
- Maintain full historical navigation context
- Perform direct, schema-enforced mutations across dependent entities