Tables
A table represents an entity in Minyu’s domain model. Each table stores multiple rows, and each row corresponds to one item of that entity. Tables also include system-managed metadata used internally for synchronization, traceability, and form generation.
Creating a table
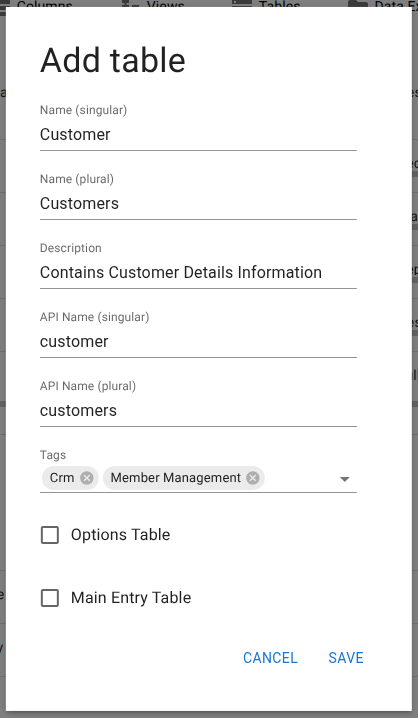
Tables are created from Database → Tables. Use the add button to define a new table. Minyu requires the following fields:

- Name (singular / plural): Human-readable labels used throughout the UI.
- API name (singular / plural): Identifiers used in API calls. Must be lowercase, may include numbers and underscores, and cannot start with a number.
- Description: Optional context for administrators.
- Tags: Optional labels used for grouping and filtering tables.
- Options table: Use for static value sets that rarely change (for example, Gender). Only administrators may edit these.
- Main entity table: Makes the table available to regular users when creating new records (for example, Person, not Address).
System columns
Minyu automatically adds the following metadata columns to every table:
- ID: Internal primary key.
- _ID: Optional legacy key used during migrations.
- Sys_Ins: Timestamp for creation.
- Sys_Up: Timestamp for last update.
- Sys_Usr: Last modifying user.
These fields are required for consistency and cannot be removed.
Sorting
Each table defines the presentation order of its columns and relationships. This is configured via Sort Columns and Relations in the table’s menu. The order determines how Minyu’s smart forms and lists are generated.
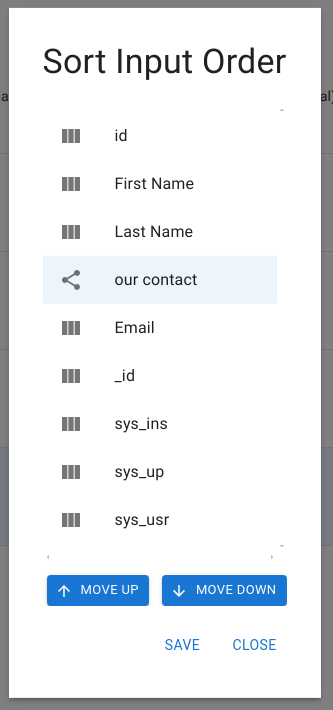
Effect of Sorting
The order you set here impacts the smart forms generated by Minyu, meaning that fields will appear in the specified order when users enter or edit data, providing a more intuitive experience.
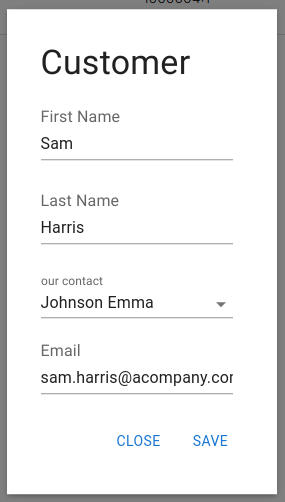
Figure: Example showing how the configured sort order affects the automatically created form
This ordering also applies in other areas of Minyu, such as lists, where fields appear in the configured sequence. By arranging columns and relationships in a logical order, such as placing "First Name" before "Last Name," you ensure a more intuitive and user-friendly experience.
By following these steps to configure tables, columns, and relationships in Minyu, you can create a structured, adaptable system that meets your organization’s unique requirements. A well-configured domain model with appropriate rules supports high data quality, making the system easier to use and maintain over time.